

- No guesswork – A mixture of siRNAs has a better chance of success than a single siRNA design.
- No wasted time and money due to failed siRNA designs
- More regions of the genes can be screened for silencing
- Provided with the proven GeneSilencer™ siRNA Transfection Reagent
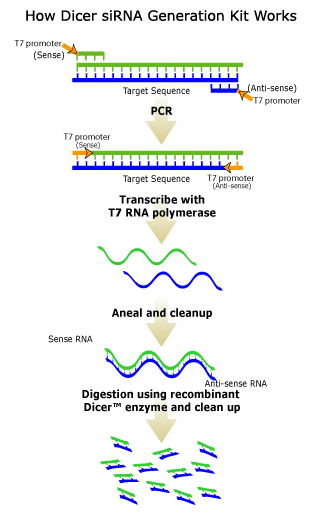
The Dicer siRNA Generation Kit provides an siRNA design tool allowing the easy and cost-effective generation of a large number of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) from full-length target genes (1). siRNAs are 21- to 23-nucleotide RNA molecules that can cause targeted gene silencing in mammalian cells through a process known as RNA interference (2,3,4). In nature, siRNAs are generated by ribonuclease III cleavage of longer double stranded RNAs (dsRNAs). When dsRNAs are transfected directly into mammalian cells, they activate the interferon system and provoke non-specific gene suppression and cytotoxic response (2). siRNAs have proven to be effective at specifically silencing gene expression without causing any interferon response.The Dicer siRNA Generation Kit mimics the natural RNA interference process by using recombinant human dicer enzyme, a double-stranded RNA-specific endonuclease, to cleave in vitro transcribed dsRNA templates into a pool of 22 bp siRNAs (Data Tab Figure 1, 2).
For maximum convenience, the Dicer siRNA Generation Kit contains everything that is required for preparing double stranded RNA, RNA cleavage, siRNA cleanup and transfection. Both the Recombinant Dicer Enzyme and the RNA Purification Columns are also available separately.
ContentsSufficient material is provided for transcribing, cleaving, and transfecting siRNAs for 50 transfection experiments in 24-well plates and with up to 5 different genes.
StorageThe Dicer siRNA Generation Kit is shipped frozen. Both the TurboScript™ T7 Transcription Kit and the recombinant human dicer enzyme should be stored at –20°C upon receipt. If stored properly, all reagents are stable for 6 months.
New CitationsA novel mechanism of lncRNA and miRNA interaction: CCAT2 regulates miR-145 expression by suppressing its maturation process in colon cancer cells.Yu, Y., et al (2017) Mol. Cancer 16(1): 155. Link
Human Virus-Derived Small RNAs Can Confer Antiviral Immunity in Mammals.Qui, Y., et al Qui, Y., Link
Low active loading of cargo into engineered extracellular vesicles results in inefficient miRNA mimic delivery.Sutaria, D.S., et al (2017) J. Extracell. Vesicles 6(1): 1333882 Link
Rational design of novel N-alkyl-N capped biostable RNA nanostructures for efficient long-term inhibition of gene expression.Terrazas, M., et al (2016) Nucleic Acids Res. 44(9): 4354-4367. Link
Yellow fever virus capsid protein is a potent suppressor of RNA silencing that binds double-stranded RNA.Samuel, G.H., et al (2016) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 113(48): 13863?13868. Link
Bioengineering Novel Chimeric microRNA-34a for Prodrug Cancer Therapy: High-Yield Expression and Purification, and Structural and Functional Characterization.Wang, W-P., et al (2015) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 354(2): 131?141. Link
Nucleotide sequence of miRNA precursor contributes to cleavage site selection by Dicer.Starega-Roslan, J., et al (2015) Nucleic Acids Res. 43(22): 10939?10951. Link
Key elements of the RNAi pathway are regulated by hepatitis B virus replication and HBx acts as a viral suppressor of RNA silencing.Chinnappan, M., et al (2014) Biochem J. 462 (2): 347-358. Link
Synthetic pre-microRNAs reveal dual-strand activity of miR-34a on TNF-α.Guennewig, B., et al (2014) RNA 20(1): 61-75. Link
Kaposi抯 Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus MicroRNA SingleNucleotide Polymorphisms Identified in Clinical Samples Can Affect MicroRNA Processing, Level of Expression, and Silencing Activity.Han, S-J., et al (2013) J. Virol. 87(22): 12237?12248. Link
Dicer siRNA Generation Kits
- Dicer siRNA Generation Kit - 1 kit, T510001
- TurboScript T7 Transcription Kit - 20 rxns, T510003
- RNA Purification Column 1 - 20 columns, T510004 (ships room temp)
- RNA Purification Column 2 - 20 columns, T510005 (ships room temp
For maximum convenience, the Dicer siRNA Generation Kit contains everything that is required for preparing double stranded RNA, RNA cleavage, siRNA cleanup and transfection. Both the Recombinant Dicer Enzyme and the RNA Purification Columns are also available separately.

Preparation of siRNA cocktails: Dicer or RNAse III?
IntroductionSmall interfering RNA (siRNA)-mediated gene silencing has become a valuable and exciting area of research.Since its inception (1), the design of synthetic siRNAs has been greatly improved over the initial random 揾it and miss? approach.Presently, investigators use various algorithms to identify within an open reading frame (ORF) a 22bp sequence that may or may not activate the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC).In some instances, these algorithms have been shown to be effective (2), but there are improvements to be made.Often the chemically synthesized algorithm-derived siRNA molecule has no efficacy in gene silencing, leaving the investigator little choice but to synthesize additional 22bp siRNA candidates.This can be time consuming and costly because the rules for effective siRNA design are not yet well established.An alternative approach is to synthesize, in vitro, dsRNA from the entire ORF of interest and cleave the resulting transcripts with human recombinant Dicer or escherichia coli RNAseIII producing a cocktail of siRNAs (3,4).Dicer is an endo-ribonuclease that contains RNAseIII domains, and is the enzyme that cleaves long dsRNAs in the endogenous RNAi pathway (5).The RNAseIII enzyme is involved in the maturation of cellular phage and plasmid RNAs (6).The siRNAs produced by the Dicer enzyme are approximately 21-23 bp in length, whereas the cleaved products of RNAseIII range from 12-15 bp.These enzymatically-generated cocktails of siRNA can be easily transfected (using a reagent such as GeneSilencer?) as part of RNA interference experiments.The method of using Dicer or RNAseIII for in vitro generation of siRNA is attractive for two reasons: 1) low cost, due to the fact that screening a number of different individual siRNA candidates is not necessary, and 2) almost invariable gene silencing efficacy.
In order to compare the gene-silencing efficacy of siRNA generated by both Dicer and RNAseIII, we used two model systems.Initially we used, in separate reactions, either a Dicer or an RNAseIII siRNA cocktail to silence the luciferase gene in a 293-cell line stably expressing the luciferase enzyme.This approach allowed us to quantify the extent of silencing induced by the respective siRNA cocktails using a standard luciferase assay.In the second set of experiments we produced GAPDH siRNA using Dicer or RNAseIII and measured the gene silencing effect after transfection by Western blot analyses.The data presented here strongly suggests that siRNA produced by Dicer is very homogeneous in size and significantly more potent than siRNA generated by RNAse III.The implications of these results are discussed in relation to utility and application to gene silencing manipulations in cell biology.
Materials and Methods Preparation of siRNA Gene-specific polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers were synthesized with at least 20 bases of target DNA sequence.At the 5? end of each oligonucleotide, T7 RNA promoter sites were added such that when used in a PCR reaction, the resulting amplicons were flanked by T7-promoter sequences.Primers were designed for amplification of the initial 500 base pairs (bp) of the luciferase ORF and the entire 1500 bp of the GAPDH ORF.The PCR products were purified and subjected to an in vitro transcription assay using the TurboscriptTMT7 Transcription Kit (Genlantis) to generate dsRNA.The dsRNA was purified via the lithium chloride method, and 15 μg of corresponding dsRNA were digested in a Dicer reaction (Gene Therapy Systems, Inc) for 16 h, or RNAseIII reaction (Ambion) for 1 h as per the manufacturer抯 recommendations.The resulting siRNA were purified using a two-step column procedure (Genlantis) and stored at ?20 C until further use.
Transfections HEK 293-luc cells (3) were sub-cultured into a poly-D-lysine coated 96 well plate at a density of 15,000 cells/well (50%-70% confluency) and incubated overnight at 37 C with 5% CO2 in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS/1x NEAA and L-glutamine.For each well, 125 ng of siRNA (or 10nM for synthetic luciferase siRNA) was mixed with 2.5 μl of GeneSilencer? siRNA Diluent (Genlantis) and 15 μl of serum-free media (SFM).After incubating at room temperature for 5 min, a mixture containing 1 μl of GeneSilencer? (Genlantis) reagent and 25 μl of SFM was added to the diluted siRNA, and lipoplexes were allowed to form for another 5 min at room temperature.Meanwhile, the cells were washed once with PBS, and after the 5 min incubation period the total volume was brought up to 100 μl with SFM and immediately pipetted onto the cells of each well.The plates were then placed back at 370C with 5% CO2 and incubated for 4 h.After 4 h, a 20% solution of DMEM was prepared and 100 μl added to each of the transfected wells.
Western BlottingAfter a 24 h incubation period, the cells were washed once with PBS and lysed with the addition of 1X Laemmili sample buffer (7).Lysates were separated via 4%-20% gel electrophoreses under reducing conditions.Proteins were transferred via electro-blotting onto nitrocellulose and the membrane analyses were carried out using the Western Pro Kit (Genlantis) and the appropriate antibodies.
Luciferase AssayThe luciferase assay was performed using the Luciferase Assay System (Promega).Briefly, the cells were harvested 24 h post transfection and lysates were prepared as per the manufacturer抯 instructions.A 1:5 dilution of cell lysate was prepared in cell lysis solution and 10 μl was added to a plate containing 50 μl of luciferase assay reagent (LAR).The light emission was measured using the Tecan Genios luminometer and data was interpreted via Magellan software.
Results
Comparison of the siRNA Produced Using Dicer or RNAse III Enzymes Double stranded RNA was generated from templates of the GAPDH ORF (1.5 kbp) and the 5? end (500 bp) of the luciferase ORF that resulting in dsRNA of 1500bp and 500bp, respectively (data not shown).An equal amount of each dsRNA was incubated with appropriate amounts of RNAseIII or Dicer enzymes as recommended by the manufacturers.The products of the reactions were separated by 20% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and visualized using ethidium bromide.Figure 1 shows the corresponding siRNA produced by Dicer and by RNAseIII.Panel A shows the Dicer or RNAseIII generated luciferase siRNA, and panel B shows the Dicer or RNAseIII generated GAPDH siRNA.Collectively, Figure 1 shows that Dicer-generated siRNAs (lanes 2 in Panel A and B) are more homogeneous with respect to size when compared to the heterogeneous siRNA produced by the RNAseIII enzyme (lanes 1 in Panel A and B).Furthermore, Figure 1 (Panel B, lane 1) also shows that when a large dsRNA molecule is used (1500 bp GAPDH), the siRNA produced by RNAseIII is more heterogeneous in size when compared to the siRNA product generated from the digestion of a 500bp dsRNA molecule by RNAseIII.
Quantitative analyses of luciferase gene silencingThe luciferase siRNA produced by Dicer or RNAseIII were used to transfect 293-luc cells in a 96-well tissue culture plate.After 24 hours the cells were harvested and lysates were prepared for either the detection of luciferase activity or GAPDH and actin expression by western analyses.The results in Panel A of Figure 2 show lysates from cells transfected with Dicer- or RNAseIII- generated luciferase siRNA.Controls were cells that were mock transfected with transfection reagent only.The far right hand bar represents the luciferase activity of cells transfected with commercially available synthetic luciferase siRNA.The generated luciferase activity data is normalized to protein content and are displayed as relative light units per μg of protein (RLU/μg of protein) and as a percentage of the amount of total RLU/μg of protein, measured in mock-transfected cells.The results indicate that Dicer generated siRNA is 17% more efficient at gene silencing when compared to an equivalent siRNA cocktail produced by the RNAseIII enzyme.Panel B of Fig 2 indicates that non-specific silencing effects were not detected by Western analyses of GAPDH and actin suggesting that, at least in this case, the luciferase siRNA cocktails produced by either Dicer or RNAseIII to not have deleterious effects on normal cellular functioning.
Qualitative analyses of GAPDH gene silencing In similar experiments to those described above, GAPDH siRNA was transfected into 293-luc cells.However, in this case, the amount of GAPDH silencing was visualized by western analyses and non-specific effects on luciferase and actin were likewise tested.The results in Figure 3 show that for GAPDH, qualitative analyses of the extent of gene silencing reveals that Dicer-generated siRNA is more potent when compared to siRNA produced by RNAseIII.Furthermore, there are no apparent effects of GAPDH siRNA on the expression of actin or luciferase, implying again that siRNA cocktails are specific at gene silencing.
Discussion
Since both RNAseIII and Dicer have been used to produce siRNA in vitro, the aim of this study was to determine which enzyme generated the most efficacious siRNA.As our model systems, we used both luciferase and GAPDH expression to test the efficacy of Dicer or RNAse generated siRNA.The results presented here strongly suggest that siRNA produced by an in vitro reaction of dsRNA with Dicer enzyme are more potent inducers of gene silencing.We have shown in both a quantitative (luciferase assay) and a qualitative assay (western analyses) that Dicer-generated siRNA is more efficient at gene silencing than RNAseIII produced siRNA.
In previous studies performed by other investigators that compared Dicer and RNAseIII, results showed that both enzymes produce siRNA that have an equivalent gene-silencing efficacy (8).However, the technique used to determine gene silencing was formerly western analysis, which may not detect small differences in efficacy because of the inherent sensitivity limitations of the technique.On the other hand, a sensitive and quantitative method, such as the luciferase assay used in the present study, does have the resolution necessary to detect such differences in siRNA potency.
Some of the lower activity of RNAseIII-generated siRNA may be due to the reduced specific activity of an RNAseIII generated cocktail of siRNA.In this case, the low molar quantities of the specific 22 bp siRNA within the pool of siRNA would result in a lower overall concentration of specific siRNA in the total cocktail.As illustrated in Figure 1, a Dicer-generated siRNA cocktail contains more specific 22bp products when compared to RNAseIII-generated siRNA cocktail.Furthermore, the digestion of larger dsRNA (GAPDH, 1500 bp) with RNAseIII is more likely to produce a greater heterogeneous population of siRNA, and less 22 bp products.Large dsRNA molecules may also be more problematic for transfection.Moreover, a heterogeneous population of siRNA intended to induce specific gene silencing may, in fact, be more likely to produce non-specific and random effects such as activation of 2"5"-oligoadenylate synthetase, the antiviral response (9).
One of the disadvantages of using Dicer has been the length of time taken for the cleaving of dsRNA (usually overnight).Nevertheless, the present study shows that Dicer generated siRNA is highly size-specific, more potent than an equivalent siRNA cocktail generated by RNAse III and, is therefore unlikely to produce random non-specific effects.Consequently, the additional time taken to prepare the siRNA cocktails with Dicer is certainly worthwhile.Since a greater incubation time is the only disadvantage of using Dicer instead of RNAseIII, scientists at Gene Therapy Systems have recently focused on solving this challenge, and have reduced the time for digestion with Dicer to 2 hours (data not shown).
FiguresFIGURE 1 FIGURE 2FIGURE 3
Figure Legends
Figure 1.Comparison of siRNA Generated with either RNAseIII or Dicer.Fifteen micrograms of luciferase (A) or GAPDH (B) dsRNA were digested with either RNAseIII (lanes 1) or Dicer (lanes 2) for 1 hr or overnight respectively.A sample of each siRNA was analyzed on a 20% acrylamide gel and the bands were visualized by ethidium bromide.The molecular size marker is labeled M.Figure 2.Transfection of HEK 293-Luc cells with Luciferase siRNA.Luciferase siRNA was generated with either Dicer or RNAseIII and transfected into HEK 293-luc cells, incubated for 24 h and lysates were prepared for a Luminescence assay (Panel A) or Western analyses (Panel B).Panel A represents the Relative Lights Units per μg of protein (RLU/μg) expressed as a percentage of the activity of mock transfected cells (Cells only) against cells transfected with either Dicer or RNAseIII generated siRNA.Controls are mock-transfected cells (siRNA only), untreated cell (cells only) and cells transfected with synthetic siRNA (syn siRNA, Dharmacon).In Panel B lane 1 represents cells transfected with Dicer generated siRNA and lane 2 represents cells transfected with RNAseIII.Lanes 3, 4 and 5 are controls representing mock-transfected cells, untreated cells and cells transfected with synthetic siRNA (Dharmacon) respectively.The proteins detected on the individual immunoblots are indicated on the right. Figure 3.Transfection of HEK 293-Luc cells with GAPDH siRNA.GAPDH siRNA was generated with either Dicer or RNAseIII and transfected into HEK 293-luc cells, incubated for 24 h and lysates were prepared for Western analyses.Lane 1 represents cells transfected with Dicer generated siRNA and lane 2 represents cells transfected with RNAseIII.Lanes 3 and 4 are controls representing mock-transfected cells and untreated cells respectively.The proteins detected on the individual immunoblots are indicated on the right.Genlantis位于美国加利福尼亚州的圣地亚哥,是基因治疗系统公司的分公司。Genlantis致力于体内和体外诊断蛋白表达工具的研发及高效传递技术的开发。Genlantis为全球的生命科学研究客户生产研发生物学试剂,包括基因传递和质粒DNA的转染试剂(GenePORTER®),哺乳动物细胞siRNA转染试剂(GeneSilencer®),原代神经元细胞的优化转染试剂(NeuroFECT®)和原代神经细胞的转染试剂(NeuroPure®)。此外,我们还是Tap Express®和Xi-Clone® Instant Enzymeless PCR克隆技术的持有者。这些技术使得科学家们可以同时设计成百上千的蛋白,还可把成本控制在理想的范围内;可以使科学家们由复杂的细菌感染比如疟疾,肺结核,炭疽,天花病毒,衣原体,螺杆菌等快速的制备出相应的蛋白。













